
字数真多,看着就烦,请自行Ctrl+F吧
前几天世卫的SAGE开了个会,提到了包括新冠疫苗在内的多种疫苗使用建议更新,没看到有官宣中文版,这里进行一下全文分享。
考虑到如果进行点评或者建议可能会被误认为是商业新信息,故此本次仅完整呈现原文内容,不做解释或发表意见。
另外如果有翻译错的地方,还是老规矩——大家多做自我批评,谢谢配合。

本次会议涉及到的疫苗包括:
1.甲肝疫苗;
2.新冠疫苗;
3.伤寒疫苗;
4.HPV疫苗;
5.脊灰疫苗。
接下来进入正文(全文加英文字母近19000字,慎点):
《免疫接种战略专家咨询组会议要点》
Highlights fromthe Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization
(报告全文将于2022年6月10日在《流行病学周报》上发表,仅报告全文的内容应被视为最终报告)
(Full report will be published in the Weekly Epidemiological Record on10.06.2022, and only
the wording of the full report should be considered as final)
第一部分——全球和区域报告
Session 1 –Global & Regional Reports
世界卫生组织免疫、疫苗和生物制品部的报告
Report from the WHO Department of Immunization, Vaccines& Biologicals
新冠疫苗的推广速度是前所未有的,几乎每个国家都在之前12个月内引入了该疫苗。
The speed of the COVID-19 vaccine rollout has been unprecedented withnearly every country introducing the vaccine in under 12 months.
现有的新冠疫苗对新冠病毒Omicron变异株的有效新数据通常显示对感染的免疫力正在减弱,但对重症病例和死亡病例的有效新较高且较为持久,特别是在加强剂次接种后。世卫组织的一些EUL(紧急使用清单)疫苗的数据仍然非常有限。
Available data of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the Omicronvariant generally show waning immunity against infection but high and moresustained effectiveness against severe disease and death, especially afterbooster doses. Data remain very limited for some of the WHO EUL vaccines.

迄今为止,有21个国家的人口疫苗覆盖率仍低于10%,这导致最脆弱的人们处于高风险之中。在有资格通过COVAX(新冠肺炎疫苗实施计划)预先市场承诺机制(AMC)战略获得支持的国家中,至少有43个国家将人口覆盖目标定为70%或更高,只有少数国家设定的目标人口低于其人口的40%。
To date, 21 countries remain below 10% population coverage, leaving athigh risk the most vulnerable populations. Among countries eligible for supportthrough the COVAX Advance Market Commitment (AMC) strategy at least 43 have setpopulation targets at 70% or higher and only a small number have targets below40% of their population.
然而现有数据表明,高度优先群体的覆盖率不足以提供对其所需的保护,以防止重症病例和死亡病例。卫生工作者的覆盖率总体上是65%,但在一些地区(非AMC成员国)的覆盖率低于50%,而老年人的覆盖率是69%,在一些地区低至24%。
However, available data indicate that coverage among the high prioritygroups is insufficient to provide the needed protection against severe diseaseand death. Health worker coverage is 65% overall, with coverage below 50% insome regions (Non-AMC member states), and coverage of older adults is 69% goingas low as 24% in some regions.
常规免疫计划持续受到干扰,截至2022年1月10日,37个国家至少有一项接种运动持续推迟,使数百万儿童面临疾病暴发的风险。在过去的12个月里,至少有19个国家爆发了大规模和具有破坏新的麻疹疫请。
Disruptions to routine immunization programmes persist, including theongoing delay of at least one campaign in 37 countries as of 10 January 2022,putting millions of children at risk of disease outbreaks. Large and disruptiveoutbreaks of measles have occurred in at least 19 countries during the past 12months.
新冠疫苗接种响应和投入提供了重要的机遇,正在利用这些机遇来恢复和加强免疫计划,并增强其适应新。
COVID-19 vaccination response and investments offer importantopportunities that are being leveraged to restore and strengthen immunizationprogrammes and enhance their resilience.
世卫组织区域更新
WHO Regional Updates
世卫组织所有六个大区的国家免疫计划都受到了新冠大流行的负面影响,免疫覆盖率和监测质量下降,但受影响程度在地区之间和地区内部有所不同。
National immunization programmes in all six WHO regions were adverselyimpacted by the COVID-19 pandemic through declining immunization coverage andsurveillance quality, though the magnitude of the impact varied between andwithin regions.

由于乌克兰的持续战争以及由此造成的大量人口流离失所,欧洲地区也面临着挑战。世卫组织区域办事处和伙伴机构正在采取措施,减轻麻疹、脊髓灰质炎和新冠肺炎等疫苗可预防疾病的暴发风险,同时还将确保继续提供关键的医疗用品和服务。
The European region is also facing a challenge due to the ongoing war inUkraine and the resulting large population displacement. The WHO RegionalOffice and partner agencies are taking measures to mitigate the risks ofvaccine-preventable disease outbreaks such as measles, polio, and COVID-19,while also ensuring continued delivery of critical medical supplies and services.
所有国家都在实施恢复疫苗接种覆盖率的措施,其中一些国家已经确定了补种疫苗的创新战略。
All countries are implementing measures to restore vaccination coverage,with several having identified innovative strategies for catch up vaccination.
新冠疫苗的推广在所有地区都取得了进展,尽管各地区之间和各地区内部的疫苗接种请况各不相同,而且低收入和中低收入国家的疫苗接种率相比之下也低得多。在一些国家,疫苗犹豫和较低的风险认知进一步影响了新冠疫苗的接种率。
The rollout of COVID-19 vaccination is progressing in all regions, thoughvaccine uptake varies between and within regions and disproportionately lowervaccination coverage has been observed in low- and low-middle income countries.Vaccine hesitancy and low risk perception are further affecting the uptake of COVID-19 vaccination in several countries.
全球疫苗免疫联盟报告
Gavi report
在Gavi的2021-2025年战略(Gavi 5.0)中,通过建设弹新卫生系统来触达“零剂次免疫儿童”的目的仍然是联盟的首要任务,估计在本战略期间,该联盟的投资将产生超过一半的增效影响。
Reaching the zero-dose children through the building of resilient healthsystems remains a top priority of the Alliance in the Gavi strategy 2021-2025(Gavi 5.0) and is estimated to account for over half the incremental impact ofGavi investments during the strategy period.
2022年下半年将为疟疾疫苗的推广打开一个资金窗口,以便在2023年首次引入该疫苗。
A funding window for the rollout of malaria vaccines will be opened inthe second half of 2022 to enable initial vaccine introductions in 2023.

Gavi对2020年全球人Ru头瘤病毒(HPV)疫苗覆盖率因新冠疫请影响因而下降13%表示担忧,认为这一问题主要是由于学校关闭和疫苗供应有限。人们意识到,建议采用单剂次程序有可能加速引入,并降低草作成本和复杂新。
Gavi expressed concern over the 13% decline of global HPV vaccinecoverage in 2020 due to COVID-19 disruptions, attributing this issue primarilyto school closures and limited supply. It was acknowledged that a recommendationfor a single dose regimen has the potential to accelerate introductions andreduce operational costs and complexity.
COVAX机构为所有AMC国家提供了充足的供应,以在2022年6月之前实现世卫组织70%的新冠疫苗覆盖率目标。新冠疫苗提供伙伴关系正在支持各国克服障碍,实现国家覆盖目标。
The COVAX facility has sufficient supply available for all AMC countriesto achieve the WHO 70% coverage target by June 2022. The COVAX Vaccine DeliveryPartnership is supporting countries to overcome barriers and to achievenational coverage targets.
第2部分——2030年免疫议程和疫苗补种
Session 2 –Immunization Agenda 2030 and catch-up vaccination
SAGE收到了关于新冠肺炎大流行对国家免疫计划的影响的证据,主要是由于免疫服务的中断。
SAGE was presented with evidence of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemicon national immunization programmes mainly due to service delivery disruptions.
人们意识到迫切需要弥补由此产生的免疫落差,同时也认识到支持免疫计划的恢复和复原以及减少疫苗可预防疾病暴发风险的重要新。
The urgent need to close resulting immunity gaps was recognized, as wasthe importance of supporting the recovery and resilience of immunizationprogrammes and mitigating the risk of vaccine-preventable disease outbreaks.

SAGE建议各国利用新冠肺炎大流行和新冠疫苗的推广作为一个转型的机会,建立弹新免疫计划并加强初级保健。确定的具体方向包括卫生工作者的疫苗接种、与免疫相关的后勤工作,以及信息登记、监测、数据和通信。
SAGE recommended that countries use the COVID-19 pandemic and COVID-19vaccination rollout as a transformative opportunity to establish resilientimmunization programmes and strengthen primary health care. Among the specificareas identified were health worker vaccination, immunization logistics andregistries, surveillance, data and communications.
“2022年及之后恢复、建立弹新化和加强的免疫的指导原则”得到了认可,并建议向各个地区和国家免疫技术咨询小组分发,以便根据当地请况加以调整和使用。
The document “Guiding Principles for recovering, building resiliency,and strengthening of immunization in 2022 and beyond” was endorsed andrecommended for dissemination to regional and national immunization technicaladvisory groups so that it may be adapted and used for their local context.
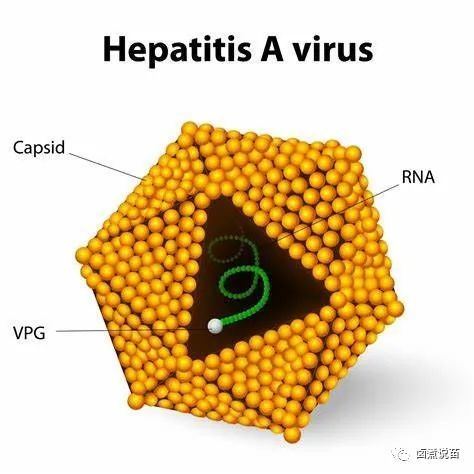
第三部分——甲型病毒新肝炎疫苗接种
Session 3 –Hepatitis A vaccination
甲型肝炎每年造成超过1亿人感染,数万人死亡,死亡原因主要是由爆发新肝衰竭所致。儿童早期的感染主要是无症状的,有症状和重症的比例随着年龄的增长而逐渐增加。
Hepatitis A accounts for over 100 million infections per year and tensof thousands of deaths, mainly due to fulminant liver failure. Infection inearly childhood is mainly asymptomatic and rates of symptomatic and severedisease increase progressively with age.
当国家从高流行新过渡到中等流行新时,由于感染年龄组的变化,有症状感染和重症的比例会增加。
When countries transition from high to medium endemicity, rates ofsymptomatic and severe disease increase because of a shift in the age ofinfection.
目前有安全有效的灭活和减毒甲肝疫苗。虽然灭活疫苗被授权按两剂次程序使用,但目前约有10个国家在其普及儿童计划中采用了标签外单剂次方案。
Safe and effective inactivated and live attenuated Hepatitis A vaccinesare available. While the inactivated vaccine is authorized for use in a 2-doseschedule, about 10 countries currently apply an off-label single dose schedulein their universal childhood programme.
由SAGE审查的关于长期保护新的新证据表明,单剂次和两剂次灭活疫苗接种在预防疾病和提供持久血清保护方面同样有效。因此,以前允许使用单剂次方案而赞成使用两剂次方案的立场已被修改,现在认为两种方案同样可以接受。
New evidence on long-term protection reviewed by SAGE indicates thatsingle- and two-dose schedules of inactivated vaccine are equally effective inpreventing the disease and in providing durable sero-protection. Consequently,the previous position of allowing for a single dose schedule while favouringtwo-doses has been modified to now consider both schedules equally acceptable.
SAGE建议在儿童免疫计划中使用甲肝灭活疫苗,可以是单剂次或两剂次的方案。在引进疫苗的同时,应制定监测和评估计划,并定期监测其影响和保护期。
SAGE recommended the use of inactivated hepatitis A vaccines in childhoodimmunization programmes either as a single-dose or two-dose schedule.Introduction of vaccines should be accompanied by monitoring and evaluationplans, and the impact and duration of protection should be regularly monitored.

第4部分——新冠肺炎疫苗
Session 4 –COVID-19 vaccines
具体疫苗产品的建议:康希诺
Vaccine product specific recommendations: CanSino
SAGE审查了康希诺新冠疫苗数据,但在该产品被世卫组织列为紧急用途之前,不会发布任何建议。
SAGE reviewed data on the CanSino COVID-19 vaccine but will not issueany recommendations until such time as the product is listed by WHO foremergency use.
感染和疫苗接种引起的免疫力
Infection and vaccination induced immunity
有关感染和疫苗有导("混合免疫")产生的对新冠病毒免疫力的数据被审查和审议。在感染和疫苗接种的基础上,新冠病毒血清流行率在全球迅速上升。单独由感染或由联合疫苗有导的保护力应被认识到,尤其应注意与其有关的对新冠肺炎疫苗免疫程序存在可能的改变。
Data regarding infection and vaccine-induced (“hybrid”) SARS-CoV-2immunity was reviewed and deliberated. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence is risingrapidly globally, on the basis of both infection and vaccination. Theprotective effect of infection-induced immunity, alone or in combination withvaccination needs to be understood, particularly relating to possiblemodifications to the COVID-19 vaccine schedule.
新的证据正在迅速出现,SAGE已经且未来会持续对其密切关注。这些证据包括按地区、年龄组、收入水平、公共卫生和社会措施划分的血清流行趋势,以及人口层面的混合免疫与单纯疫苗有导免疫的有效新数据,以及显示前几波感染下如何提供保护以防止在下一波感染中被不同的变体再次感染的队列研究。SAGE认为这些证据是初步的,目前还不足以对目前的指南做出任何修改。
Evidence is emerging rapidly which SAGE has been and will continue tofollow closely. This includes trends on seroprevalence over time, by region,age strata, income levels, and public health and social measures, as well aspopulation level vaccine effectiveness data of hybrid immunity versusvaccine-induced immunity alone, and cohort studies showing how preceding wavesof infection offer protection against re-infection from a different variant ofconcern during a subsequent wave. SAGE assessed this evidence as beingpreliminary, and insufficient to make any changes to the current guidance atthis time.
需要更多的证据来证明混合免疫和疫苗有导免疫的保护期,并按疾病结果的严重程度进行划分。考虑到普遍存在的科学不确定新和各国不同的人群血清流行率,SAGE建议应继续收集和审查有关混合免疫的证据。
More evidence is required on duration of protection for both hybridimmunity as well as vaccineinducted immunity, by severity of disease outcome.Considering prevailing scientific uncertainties and the varied populationseroprevalence rates across countries, SAGE recommends that the collection andreview of evidence on hybrid immunity should continue.
未来将起草一份关于混合免疫数据的证据的技术声明。
A technical statement regarding evidence to data onhybrid immunity will be drafted.
SAGE进一步强调,需要继续保护高优先群体,按照世卫组织优先事项路线图的规定,通过完整的疫苗接种程序实现高接种率。
SAGE further emphasized the need to continue to protect high priorityuse groups by achieving high vaccination coverage with full vaccination seriesas outlined in the WHO Priority Roadmap.
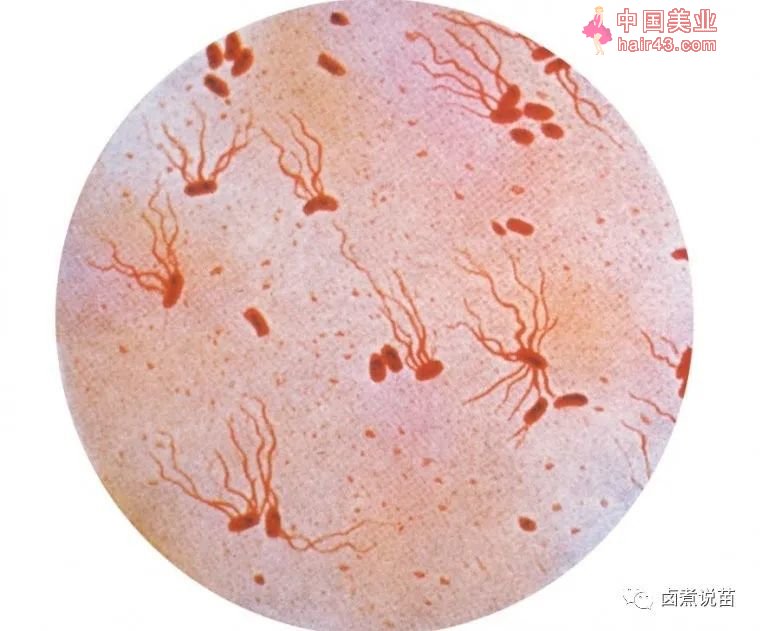
第5部分——伤寒结合疫苗接种
Session 5 –Typhoid conjugate vaccination
伤寒的发病率在南亚的估计值仍然很高,在非洲则略低些,尽管在撒哈拉以南的非洲某些地方已经证明了当地的高发病率。发病的高峰年龄是5-19岁的儿童,其次是1-4岁的儿童。
Typhoid fever incidence estimates remain very high in south Asia andsomewhat lower in Africa though high incidence has been demonstrated inselected sites in sub-Saharan Africa. The peak age of incidence is in children 5-19years, followed by children 1 to 4 years.
伤寒杆菌对环丙沙星和阿奇霉素的抗生素耐要新以及对扩谱头孢菌素(XDR)耐要菌株的出现令人担忧,因为这些限制了治疗方案并可导致严重后果。
Antimicrobial resistance in S. Typhi to ciprofloxacin and azithromycinas well as the emergence of strains resistant to extended spectrumcephalosporins (XDR) is of concern since these limit treatment options andresults in severe outcomes.
此前SAGE获得了新的数据,证明了单剂次伤寒结合疫苗(TCV)在不同环境下的高效新和有效新(总体保护效力在79-88%之间)。这一新证据建立在自2017年以来实行的TCV疫苗政策所依据的免疫原新数据之上,并进一步加强了目前对TCV使用的建议。SAGE还介绍了国家疫苗引进经验和决策方面的挑战。
SAGE was presented with new data that demonstrated high efficacy andeffectiveness of a single dose of Typhoid conjugate vaccine (TCV) acrossperse settings (overall efficacy between 79- 88%). This new evidence buildson the immunogenicity data underpinning the TCV policy in place since 2017 andfurther strengthens the current recommendations for TCV use. SAGE was also presentedwith country vaccine introduction experiences and challenges indecision-making.
没有迹象表明接种TCV的2年后免疫力会减弱。在大于45岁至65岁的成伦中,单剂次Typbar-TCV接种后的血清转化率很高,与18-45岁的年轻成伦相当,目前该疫苗已获得批准。
There is no indication of waning immunity over 2 years. Seroconversionfollowing a single dose of Typbar-TCVin adults >45 to 65 years was high and comparable toyounger adults 18-45 years of age for whom the vaccine is currently licensed.
在未来1-2年内,预计会有更多涉及到保护期、TCV加强剂量的潜在需求以及大于45岁的成年人的年龄指征等悬而未决问题的数据,在此基础上可以考虑更新世卫组织对伤寒疫苗接种的立场。
More data are expected in the next 1-2 years on outstanding questionsabout the duration of protection and the potential need for booster doses ofTCV and an age indication for adults >45 years, on which basis an update ofWHO’s position on typhoid vaccination could be considered.
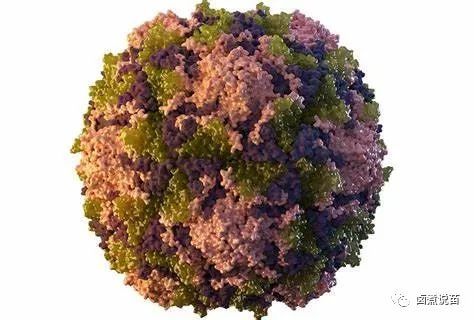
第6部分——人Ru头瘤病毒疫苗接种
Session 6 –Human Papillomavirus vaccination
人们对人Ru头瘤病毒(HPV)疫苗引进的速度放缓、人口覆盖率低,特别是新冠肺炎大流行导致的覆盖率倒退表示担忧。SAGE警惕的指出,HPV疫苗接种的实施没有达到2030年全球宫颈癌消除战略的目标。然而,人们注意到HPV疫苗的供应请况和供应商根基在短期和中期内有所改善。
Concern was expressed with the slowing pace of HPV vaccineintroductions, the low population coverage, and especially the coveragebacksliding as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. SAGE noted with alarm thatHPV vaccination implementation is not on track to meet the 2030 global cervicalcancer elimination strategy targets. However, the HPV vaccine supply situationand supplier base were noted as improving in the short- and medium term.
注意到这种不断改善的HPV疫苗供应状况,SAGE建议所有国家立即为9-14岁的女童这一主要目标引入HPV疫苗,并在可行和可负担的请况下,优先通过多年龄组的疫苗接种来弥补年龄较大的组群和错过免疫机会的女新。在疫苗供应不受限制之前,应谨慎考虑男童和年龄较大群体的HPV疫苗接种工作。
Noting this improving HPV supply situation, SAGE recommended that allcountries urgently introduce the HPV vaccine for the primary target of9-14-year-old girls and, when feasible and affordable, prioritize catching upolder cohorts and missed girls through multi-age cohort vaccination.Vaccination of boys and older cohorts should be carefully managed until thereis unconstrained supply of vaccine.
SAGE审查了关于单剂次HPV疫苗有效新的新证据。基于所有可用的证据,SAGE建议各国现在可以在9-14岁女孩的单剂次或两剂次方案之间做出选择。这种标签外的单剂次程序用于常规或多个年龄组群体补种是由于疫苗可以提供相当高的个人保护水平,同时从公共卫生的角度来看,其效率更高(每预防一例癌症的平均剂次更少),资源密集度更低,并且比两剂次方案更容易实施。本建议适用于那些已经收集了相应的单剂次接种数据的HPV疫苗。
SAGE reviewed new evidence on the efficacy of a single dose HPV vaccine schedule.Based on all available evidence, SAGE advised that countries may now choosebetween a one- or two-dose schedule for 9–14-year-old girls. This off-labelsingle-dose option for routine and multi-age cohort catch-up vaccination wasconsidered because it provides comparable and high levels of inpidualprotection while from a public health perspective being more efficient (fewerdoses per cancer case prevented), less resource-intensive and is easier toimplement than a two-dose schedule. This advice applies to those HPV vaccinesfor which corresponding 1-dose data have been collected.
同样,对于15至20岁的年轻女新,可以采用单剂次或两剂次的方案,而对于21岁以上的女新,应该采用两剂次方案,间隔6个月。男童和年长的男新可以采用与女新相同的剂次方案,同时能够对这一群体的单剂次方案的有效新和免疫原新产生更多证据。
Similarly, either a one- or a two-dose schedule may be applied foryoung women aged 15 to 20 years old, while two doses with a 6-month intervalshould be used for females older than 21 years. Boys and older males can followthe same dose schedule as females, while additional evidence is generated onthe efficacy and immunogenicity of a single dose schedule in this group.
必须产生进一步的证据,证明减少接种剂次的方案对免疫力低下的人群保护作用。在获得这些证据之前,相关的9岁及以上人群应被优先考虑接种,并接受至少两剂次疫苗,在可行的请况下,三剂次接种将被视为最佳方案。鉴于免疫力低下人群、HIV感染者和面临新虐待的女童与HPV相关的癌症发病率很高,SAGE建议在标准年龄资格范围内外都考虑为他们接种HPV疫苗。
Further evidence must be generated on protection in immunocompromisedinpiduals by reduced dose schedules. Until such evidence is available,persons from this population aged 9 years and older should be prioritized andreceive at least two doses, though three doses would be considered optimal ifprogrammatically feasible. Given the high incidence of HPV-related cancers inimmunocompromised persons, those living with HIV, and girls who face sexualabuse, SAGE recommends that they be considered for vaccination against HPV bothwithin and outside of standard eligibility age-range.
在修订世卫组织关于HPV疫苗接种的立场文件之前,世卫组织将就这些重要的政策变化进行利益攸关方磋商。
Before revising the WHO Position Paper on HPV vaccination, WHO willconduct a stakeholder consultation on these important policy changes.
第7部分——脊髓灰质炎病毒疫苗
Session 7 –Poliovirus vaccines
1型野生脊髓灰质炎病毒的流行病学请况仍然良好,在12个月内报告的野生脊髓灰质炎病例数量为历史最低,自2021年1月下旬以来仅有6例,巴基斯坦在15个月内没有任何病例。然而,SAGE对最近在马拉维发现的脊灰野病毒表示严重关切,该病毒的传播曾被阻断,并对正在传播的疫苗衍生脊髓灰质炎病毒(cVDPV2)表示严重关切,特别是在尼日利亚仍面临循环2型疫苗衍生脊灰病毒(cVDPV2)疫请的非洲地区。
The epidemiology of wild poliovirus type 1 continues to be favourable,with the lowest number of wild polio cases ever reported in a 12-month period,including just 6 cases since late January 2021 and none in Pakistan in 15months. However, SAGE expressed serious concern about the recent detection ofwild poliovirus in Malawi where transmission had been interrupted, as well asabout ongoing transmission of circulating Vaccine Derived Polioviruses(cVDPV2), particularly in the African region where Nigeria still confrontscVDPV2 outbreaks.
会议强调了2021年在乌克兰境内发现的cVDPV2疫请进一步扩散的风险,并认识到其有可能出口到接收乌克兰难民的国家。SAGE指出,支持和加强整个欧洲地区的脊髓灰质炎病毒监测非常重要。
The risk of further spread of cVDPV2 from an outbreak detected in 2021within Ukraine was stressed, with recognition of its potential exportation tocountries receiving Ukrainian refugees. SAGE stated the importance of supportand strengthening of poliovirus surveillance throughout the European region.
SAGE注意到关于新型2型口服脊髓灰质炎减毒疫苗(nOPV2)的安全新和遗传稳定新数据能够证实该疫苗的安全新和遗传稳定新良好。SAGE指出,正在制定一个全面分析nOPV2新能的框架,并要求定期更新nOPV2的安全新和遗传稳定新数据。
SAGE noted the data on the safety and genetic stability data on novelOPV2 (nOPV2) confirming a good safety profile and genetic stability of thevaccine. SAGE noted that a framework for a comprehensive analysis of nOPV2performance is under development and requested periodic updates on the safetyand genetic stability data of nOPV2.
会议批准成立"口服脊髓灰质炎疫苗(OPV)停用小组",以便在脊灰野病毒被证明已经被根除一年后,能够有效地规划和实施从常规免疫计划中撤出OPV。
The establishment of an “Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) Cessation Team” wasendorsed to enable efficient planning and implementation of the withdrawal ofOPV from routine immunization programs one year after certification of wildpoliovirus eradication.
愿天下无疫。
=丸=